Construction Techniques
Construction techniques encompass the methods and processes used to build structures and infrastructure. These techniques vary based on materials, project scale, and technological advancements. Here's a detailed overview of common construction techniques:
1. Traditional Construction Techniques
- Brick and Mortar Construction
- Method: Involves laying bricks in mortar to build walls. Mortar acts as a binding agent.
- Materials: Bricks (clay, concrete), mortar (cement, lime, sand, water).
- Applications: Residential buildings, low-rise commercial buildings.
- Advantages: Durable, fire-resistant, and offers good thermal mass.
- Wood Frame Construction

- Method: Utilizing wooden studs and beams to create a framework for the building.
- Materials: Lumber, plywood, nails, screws.
- Applications: Residential houses, small commercial buildings.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, quick to construct, and adaptable.
2. Modern Construction Techniques
- Steel Frame Construction

- Method: Erecting a skeleton frame of vertical steel columns and horizontal I-beams.
- Materials: Steel beams, bolts, concrete.
- Applications: Skyscrapers, industrial buildings, large commercial structures.
- Advantages: High strength-to-weight ratio, flexibility, and durability.
- Reinforced Concrete Construction

- Method: Pouring concrete over a framework of steel rebar or mesh to enhance strength.
- Materials: Concrete (cement, sand, aggregate, water), steel reinforcement.
- Applications: Foundations, bridges, high-rise buildings.
- Advantages: High compressive strength, fire resistance, versatility in shapes.
- Prefabricated Construction
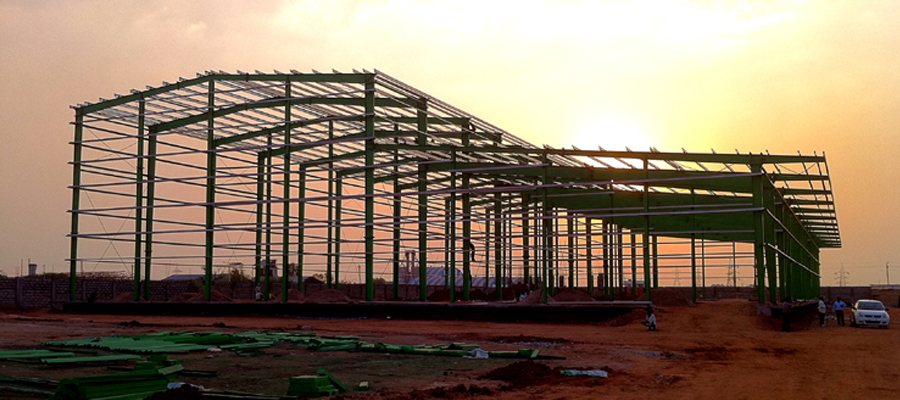

- Method: Manufacturing building components off-site and assembling them on-site.
- Materials: Steel, concrete, wood, modular units.
- Applications: Residential homes, commercial buildings, schools.
- Advantages: Reduced construction time, cost efficiency, quality control.
3. Advanced and Emerging Techniques
- 3D Printing
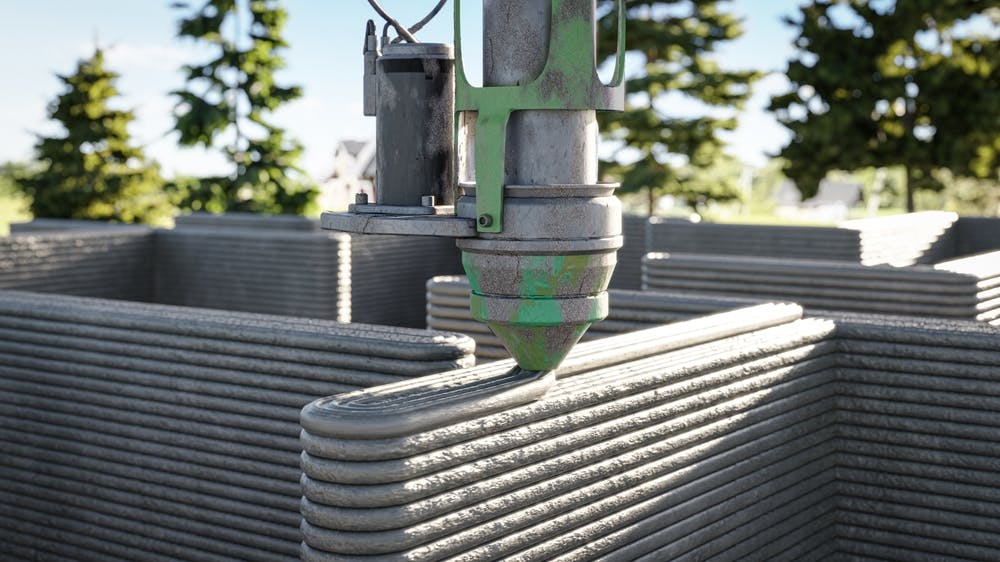

- Method: Layer-by-layer construction using a 3D printer with concrete or other materials.
- Materials: Concrete, polymers, composites.
- Applications: Small houses, custom components, experimental structures.
- Advantages: Precision, reduced waste, innovative design possibilities.
- Modular Construction
- Method: Building sections (modules) in a factory setting, then transporting and assembling them on-site.
- Materials: Steel, wood, concrete, composite materials.
- Applications: Residential buildings, hotels, offices.
- Advantages: Speed, quality control, flexibility, and sustainability.
| "Best Builders Floor Apartment in Chennai" |
4. Specialized Construction Techniques
- Green Building Techniques
- Method: Utilizing sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs.
- Materials: Recycled materials, low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) products, renewable resources.
- Applications: Eco-friendly residential and commercial buildings.
- Advantages: Environmental benefits, energy savings, health benefits.
- Tilt-Up Construction
- Method: Casting concrete panels horizontally on-site and then tilting them up into a vertical position.
- Materials: Concrete, rebar, lifting equipment.
- Applications: Warehouses, retail centers, office buildings.
- Advantages: Speed, cost-effectiveness, reduced formwork.
5. Infrastructure and Civil Engineering Techniques
- Pre-stressed Concrete Construction
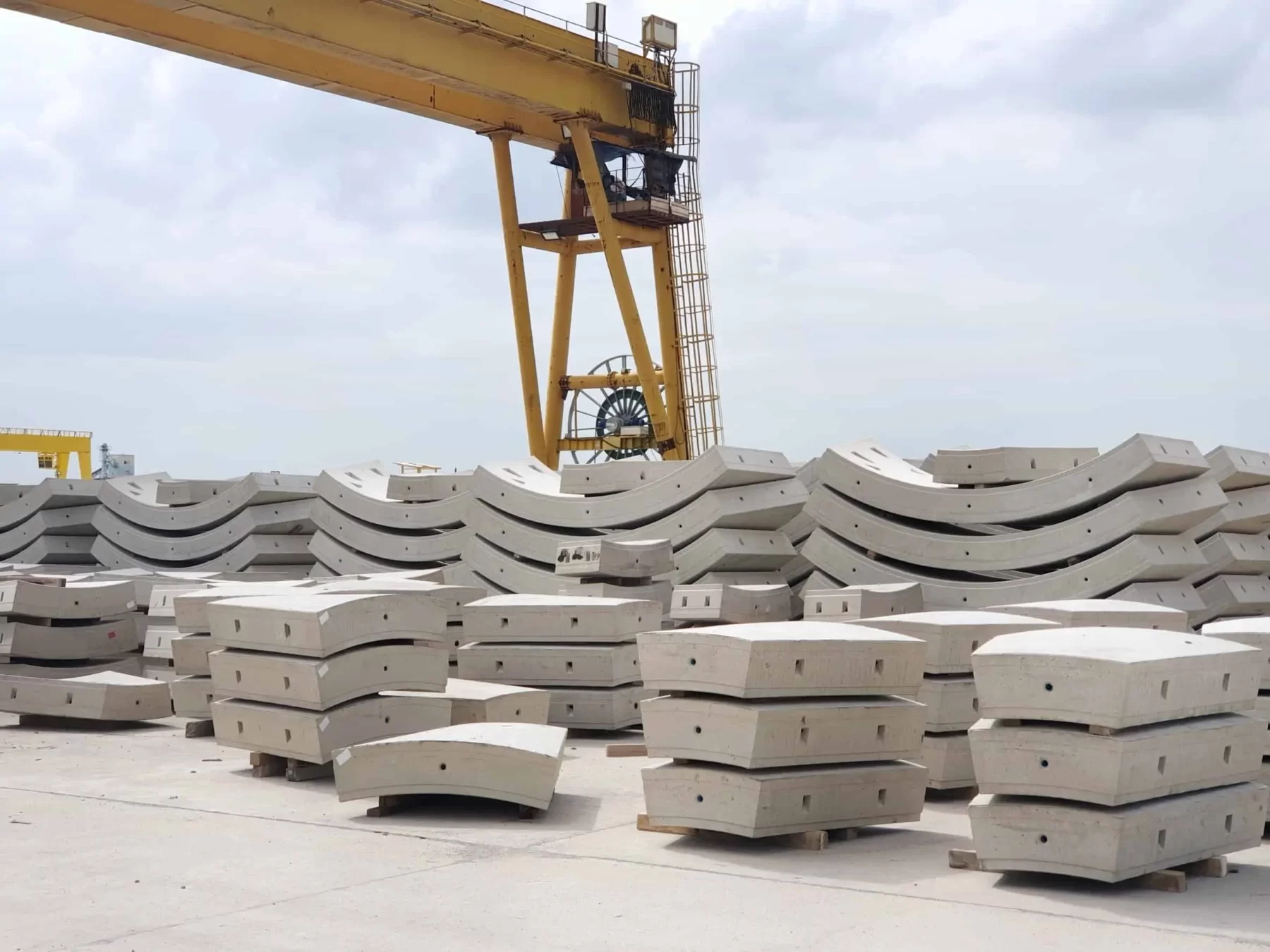

- Method: Pre-stressing concrete by tensioning the steel reinforcement before applying loads.
- Materials: Pre-stressed concrete, steel tendons.
- Applications: Bridges, parking structures, large-span buildings.
- Advantages: Greater load-bearing capacity, reduced material usage.
- Tunnel Boring
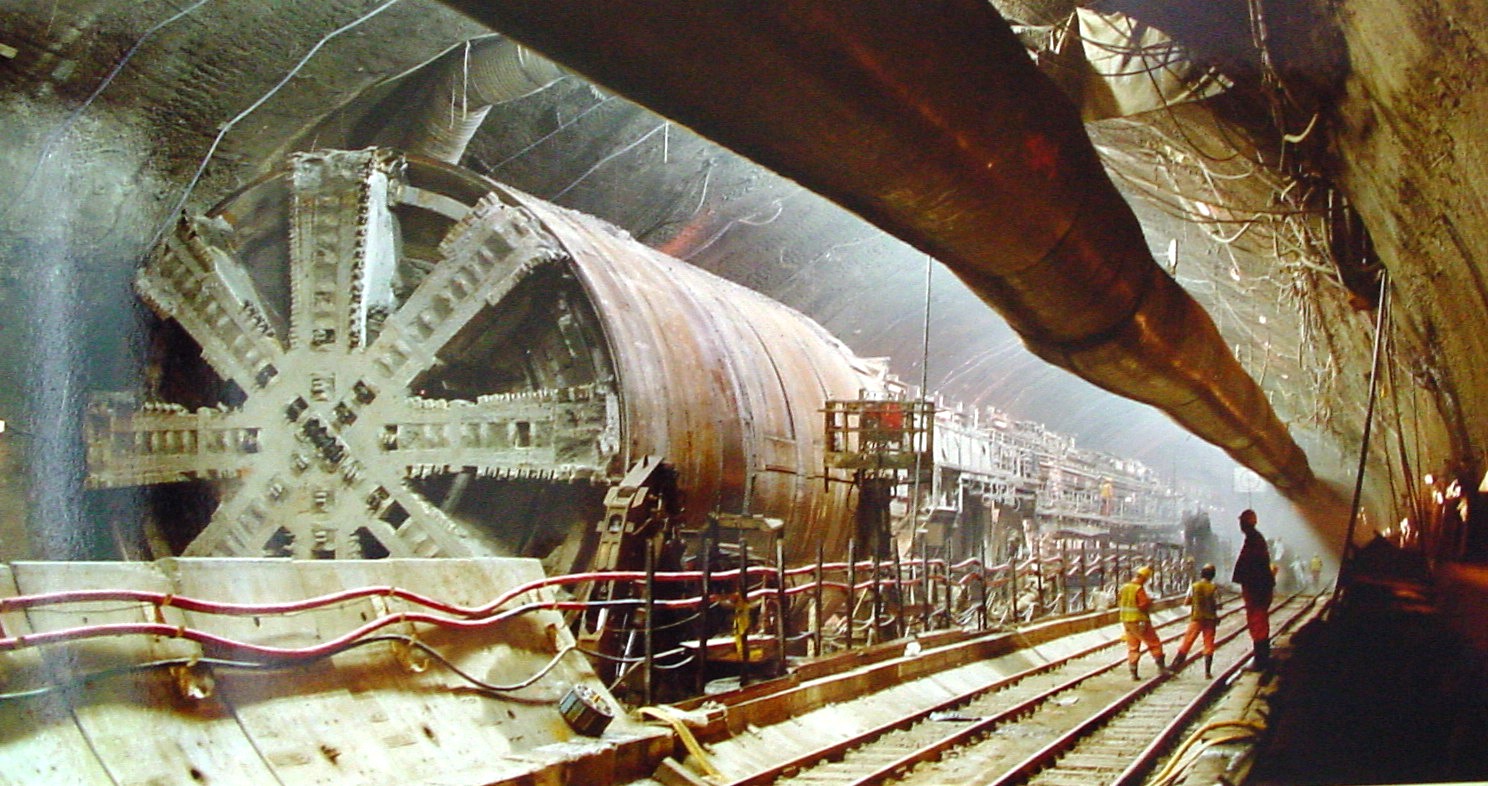

- Method: Using a tunnel boring machine (TBM) to excavate tunnels.
- Materials: TBM, concrete segments, support structures.
- Applications: Subway systems, sewer tunnels, transportation tunnels.
- Advantages: Precision, safety, efficiency in hard ground conditions.
6. Innovative and High-Tech Techniques
- Smart Building Technology
- Method: Incorporating advanced sensors, automation, and control systems into building design.
- Materials: IoT devices, automation systems, smart materials.
- Applications: Commercial buildings, residential complexes, industrial facilities.
- Advantages: Energy efficiency, enhanced security, occupant comfort.
- Nanotechnology in Construction
- Method: Utilizing nanomaterials to enhance properties of construction materials.
- Materials: Nano-silica, carbon nanotubes, nano-clay.
- Applications: High-performance concrete, self-cleaning surfaces, enhanced coatings.
- Advantages: Improved strength, durability, and functionality.
7. Construction Phases
1. Planning and Design: Involves site analysis, blueprints, permits, and planning the construction process.
2. Pre-construction: Site preparation, including clearing land, excavation, and laying foundations.
3. Construction: Actual building process, including structural, electrical, plumbing, and finishing work.
4. Post-construction: Final inspections, cleanup, and handover to the client.
Each technique has its unique applications, advantages, and constraints, shaped by the project's specific requirements, budget, and environmental considerations.
Also read: Types of Construction
/https://www.livehomes.in/blogs